In recent years, "low-altitude economy" has become a hot topic of discussion at national policies and high-level meetings. Its strategic significance has been repeatedly emphasized, and relevant policies have been successively introduced. At present, Chinas "low-altitude economy" industry is developing rapidly and has initially formed an industrial chain. However, to further form a competitive edge, it is necessary to improve the top-level design, strengthen the infrastructure construction of the low-altitude economy, deepen innovation-driven development, and continuously expand the related market demand.

01
The connotation of low-altitude economy
The concept of low-altitude economy
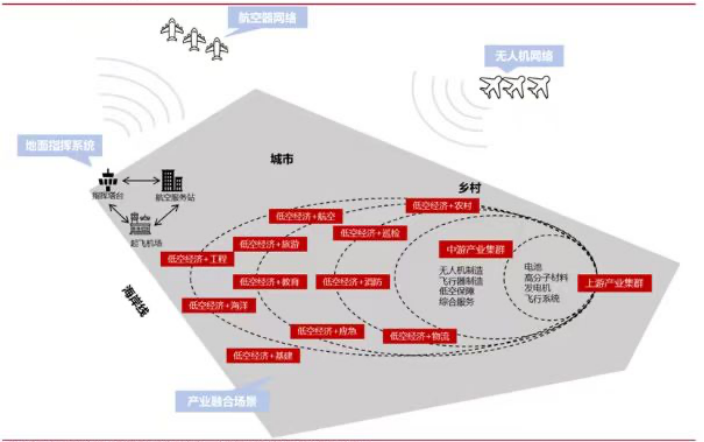
Low-altitude economy is a new economic form that relies on low-altitude airspace and takes the flight activities of various manned and unmanned aircraft as its core, radiating and driving the integrated development of related fields. Low-altitude economy, as a strategic emerging industry, is characterized by high technological content and concentrated innovative elements. It features a long industrial chain, complex application scenarios, diverse user entities, and involves numerous departments and fields. It not only encompasses traditional general aviation business forms but also integrates low-altitude production service methods supported by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Empowered by information and digital management technologies, It has integrated with more economic and social activities, forming a comprehensive economic form, which has obvious characteristics of new quality productive forces and extremely broad development space.
Interpretation of the Low-altitude Economic Industry Chain
Low-altitude economy covers the upstream, midstream and downstream of the industrial chain, forming a complete industrial system. The upstream of the industrial chain mainly consists of the fields related to raw materials and core components. The midstream of the industrial chain mainly includes the manufacturing of related products such as payloads, low-altitude products, and ground systems, as well as system services and support. The downstream of the industrial chain mainly consists of various application scenarios, including flight approval, airspace control and other various application scenarios.
Chart: Review of the Industrial Chain Structure of Low-altitude Economy
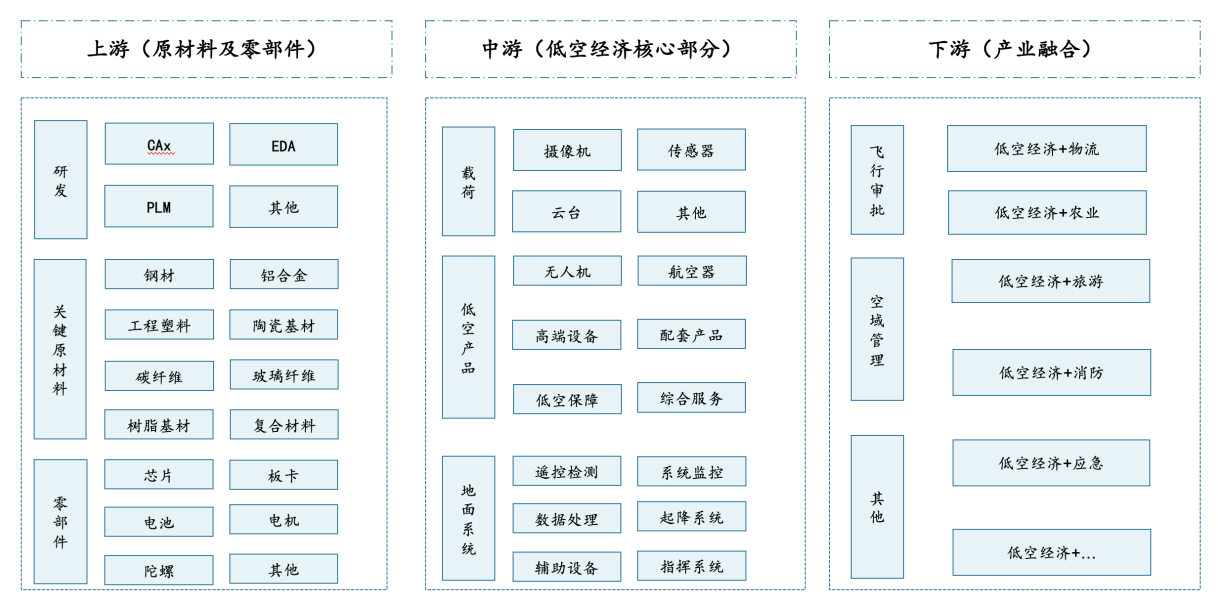
Source: Qianzhan Industry Research Institute
Key component enterprises in the upstream of the low-altitude economy industrial chain include Desay Battery, Sunwoda, Zero Degree Intelligent Control, etc. The major enterprises in aviation materials include Aviation Materials Co., Ltd. and Aviation Glass New Materials, etc. Core equipment and systems include Hangxin Technology, Andaville, etc. The midstream drone manufacturers in the industrial chain include DJI, Zongheng Co., LTD., and EHang Intelligent, etc. Aircraft manufacturing enterprises include Beidahuang, CITIC Helicopter, etc. The main aviation component manufacturing enterprises include Aero Engine Power and AVIC Electromechanical, etc. There are a large number of downstream enterprises in the industrial chain, including major airlines, logistics companies, surveying and mapping companies, construction contractors, and government departments such as fire and emergency response departments.
Chart: Ecological Map of the Low-altitude Economy Industrial Chain
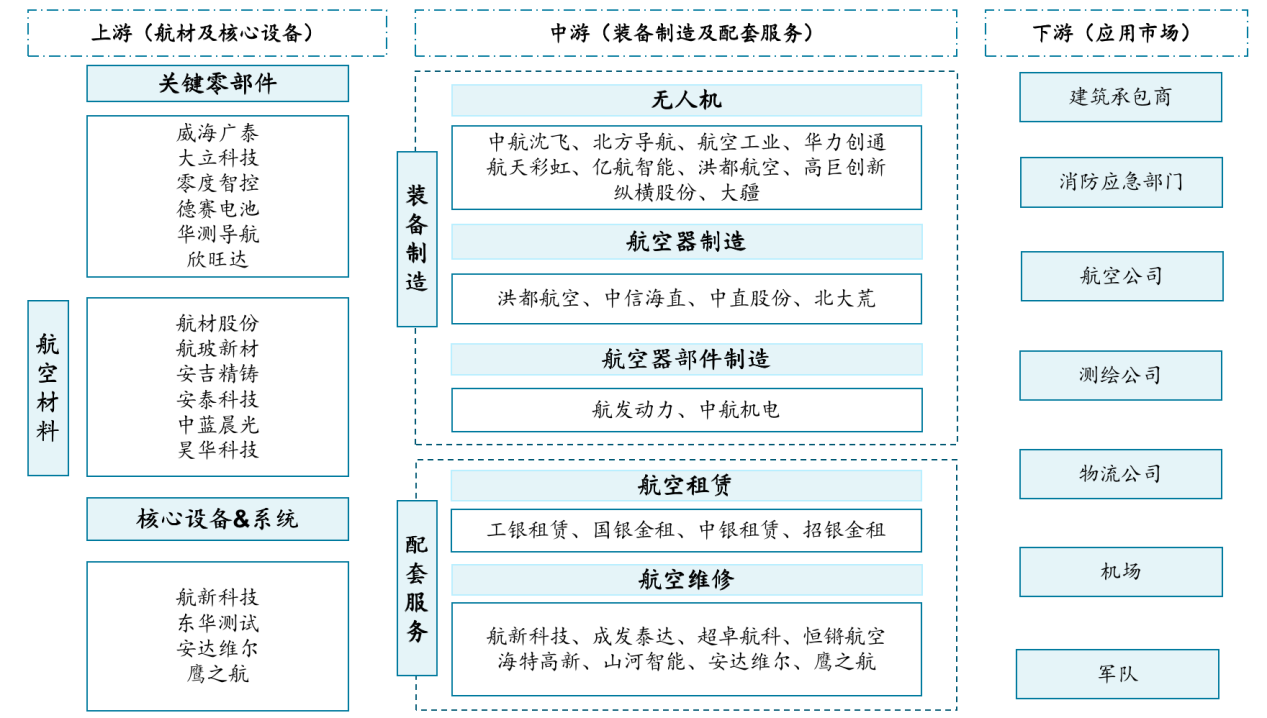
Source: Qianzhan Industry Research Institute
Twelve major industrial directions of low-altitude economy
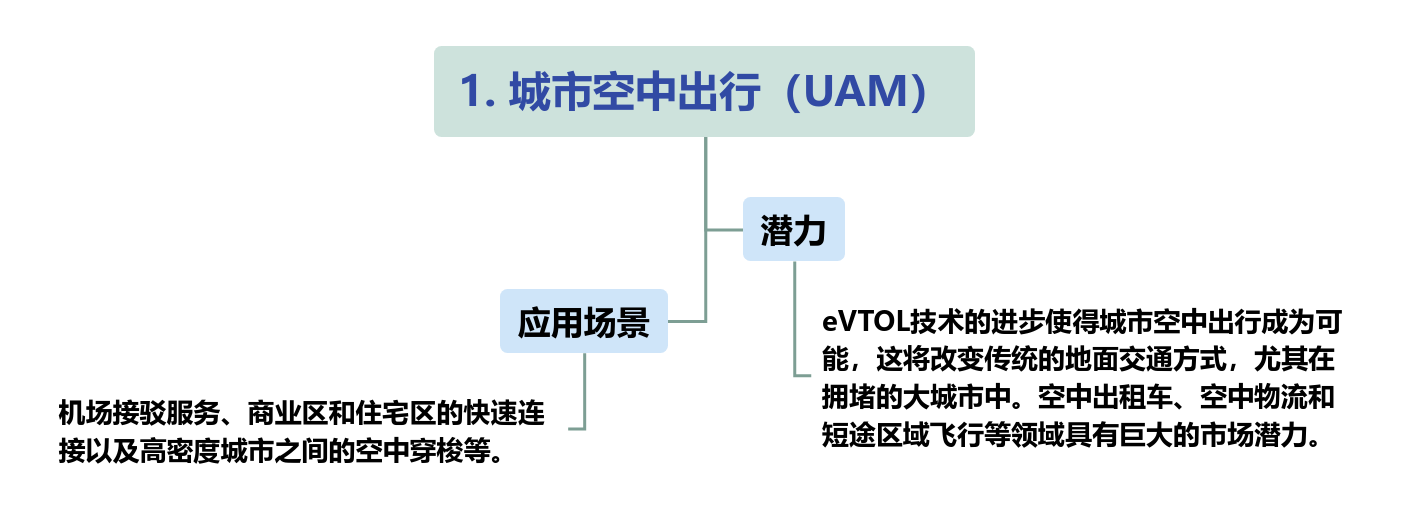
Low-altitude economy, as an emerging economic form, encompasses numerous industrial directions with development potential. Among them, there are six major directions on the application and demand side, and six major directions on the supply and construction side.
There are on the application and demand side
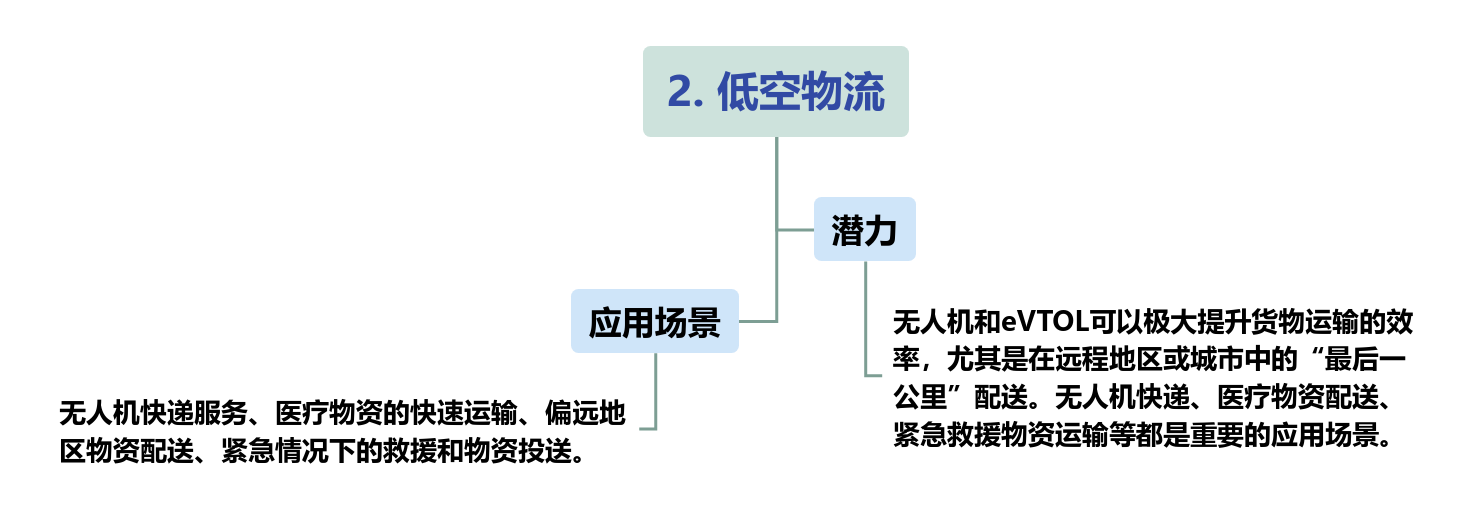
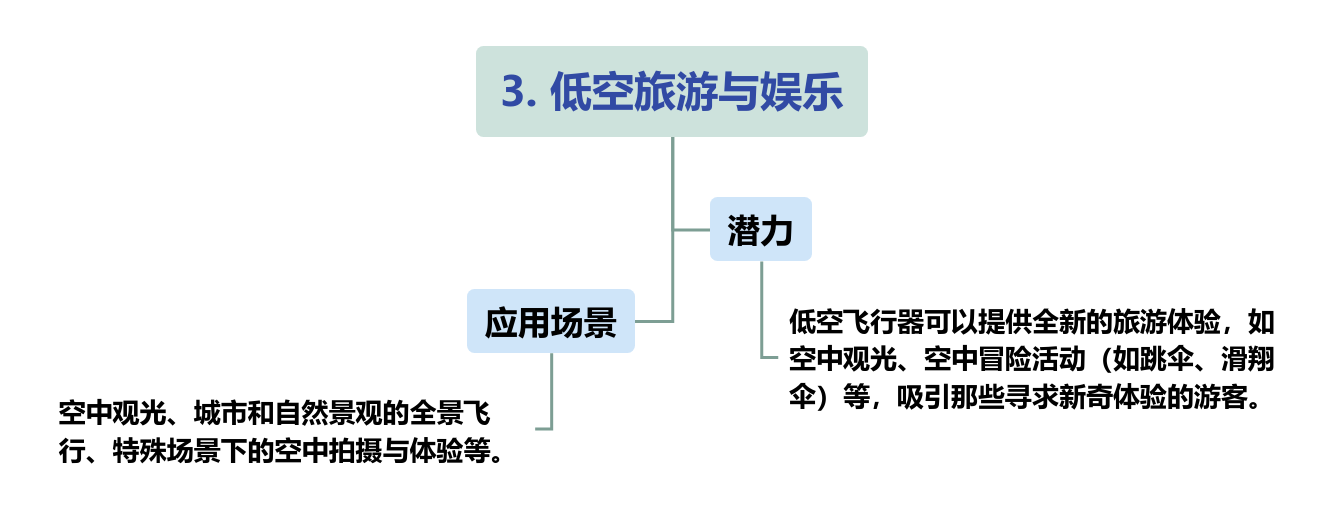
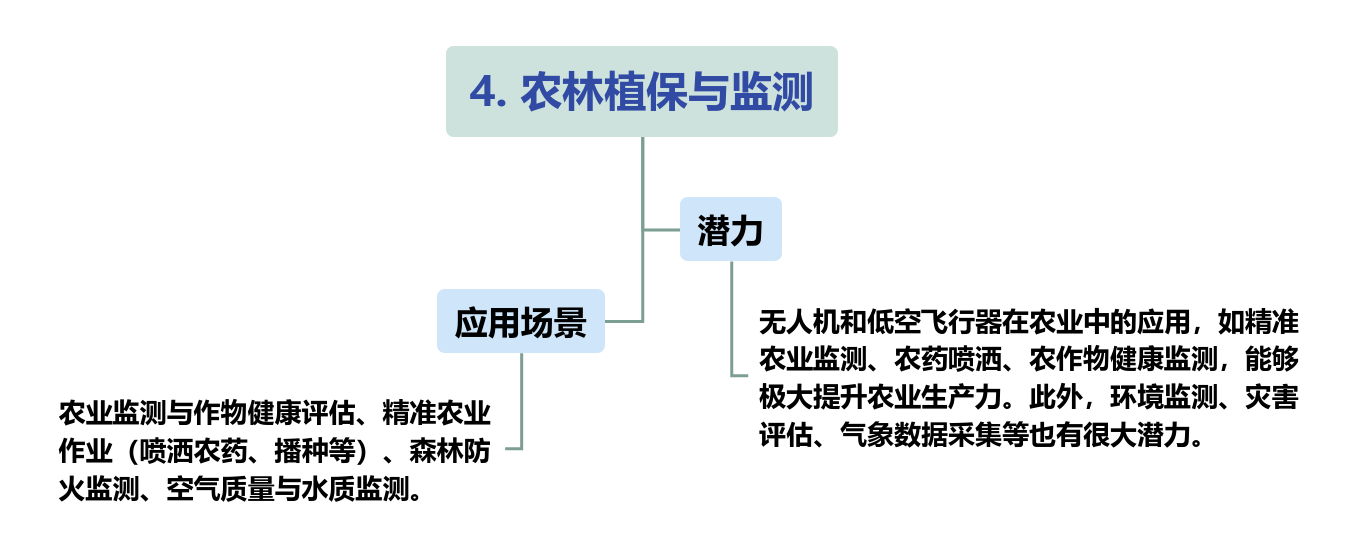
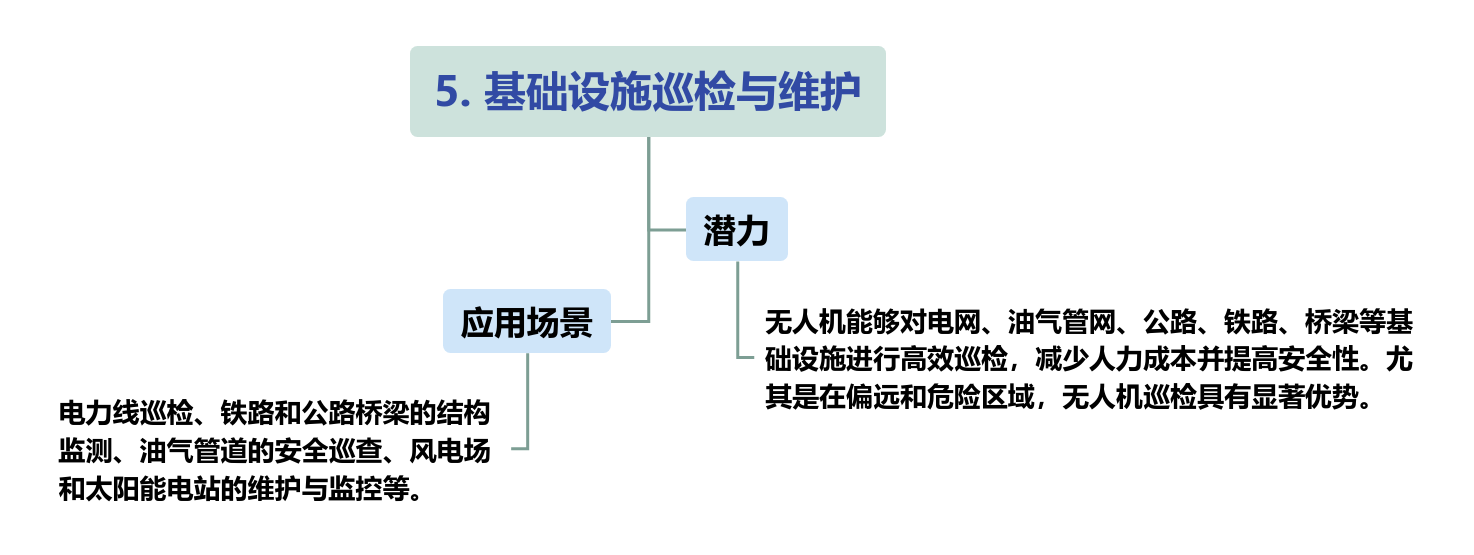
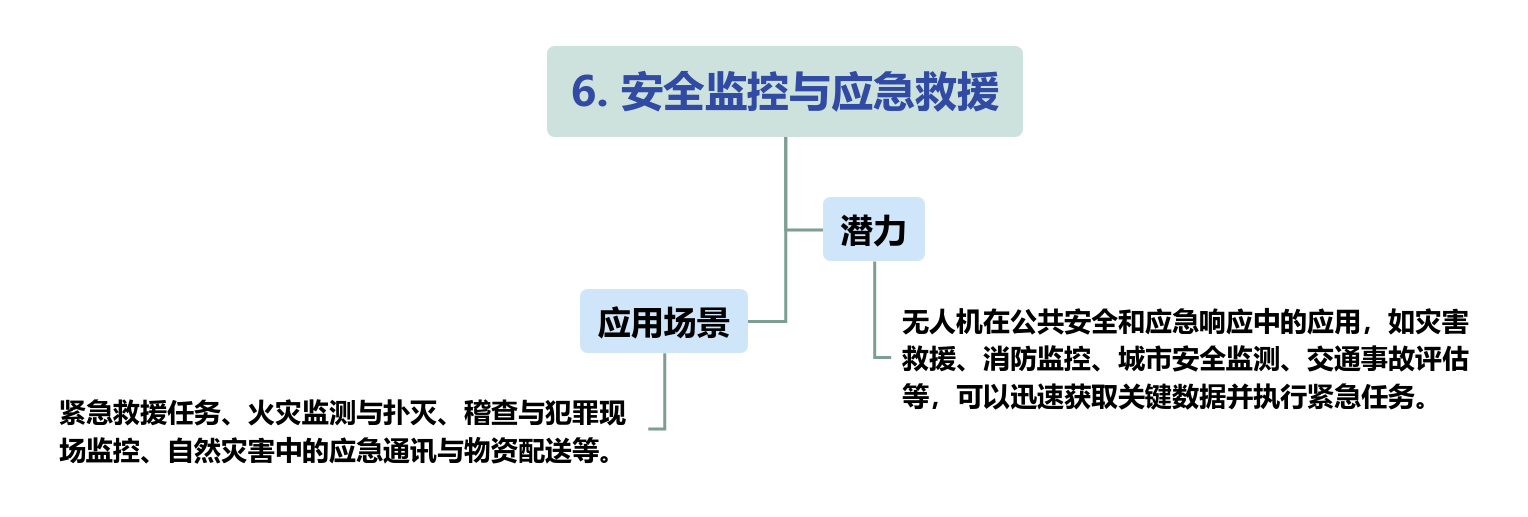
There are on the supply and construction sides
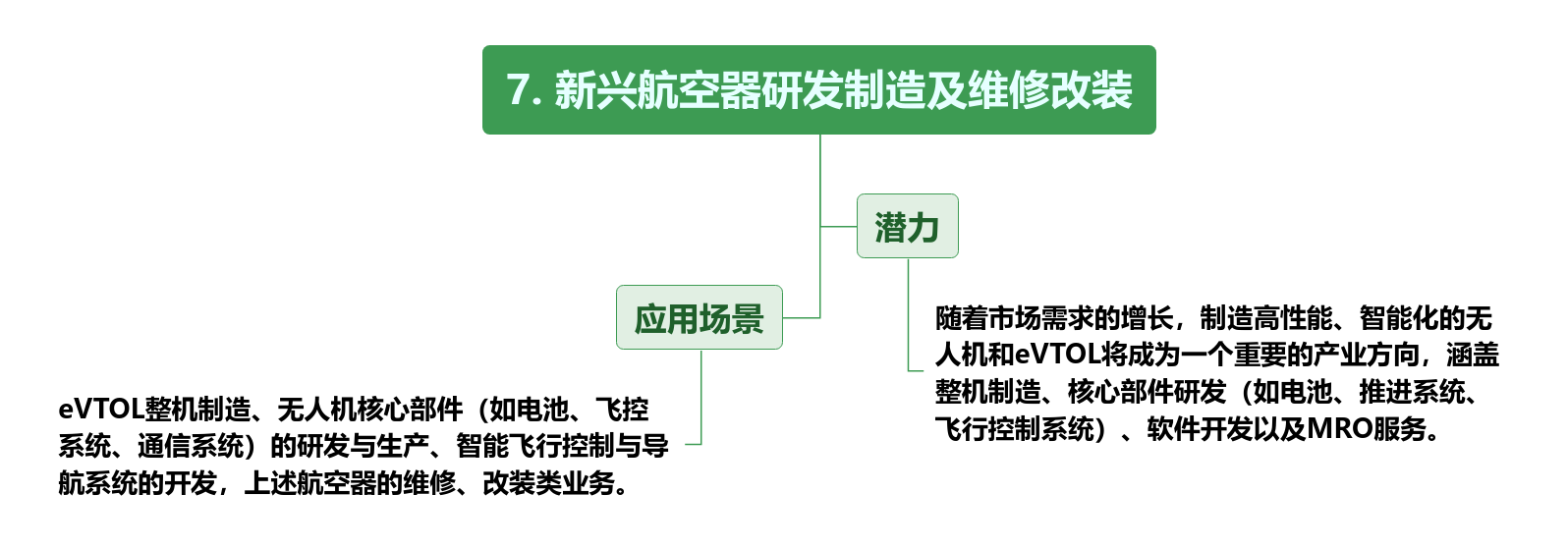
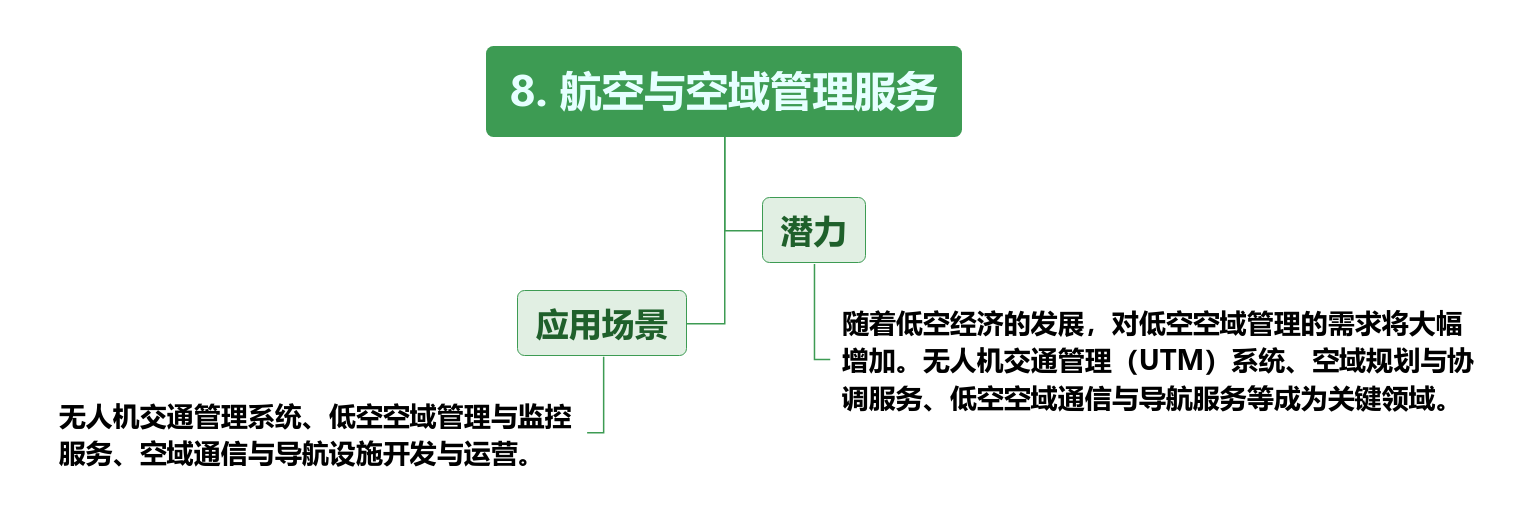
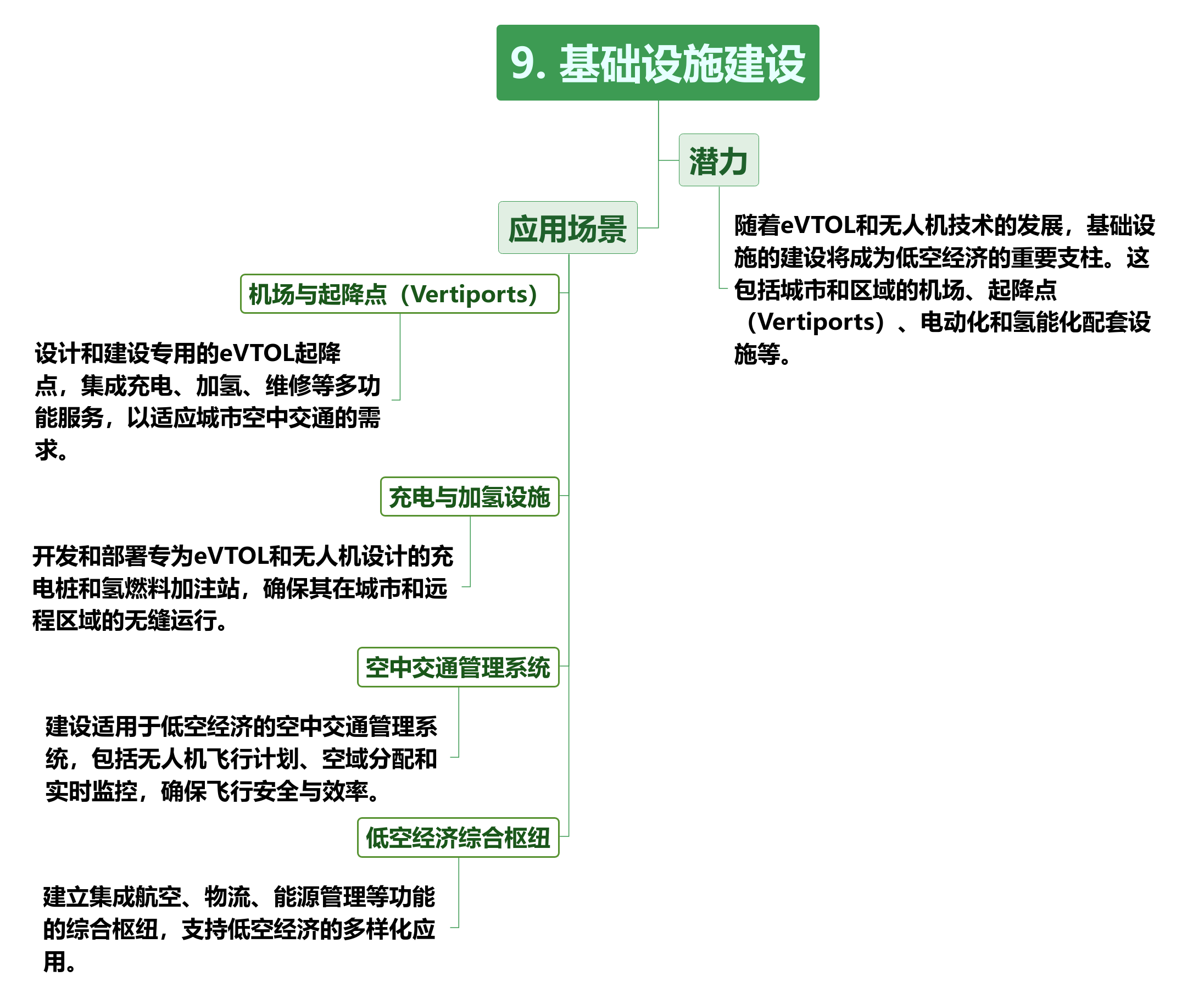
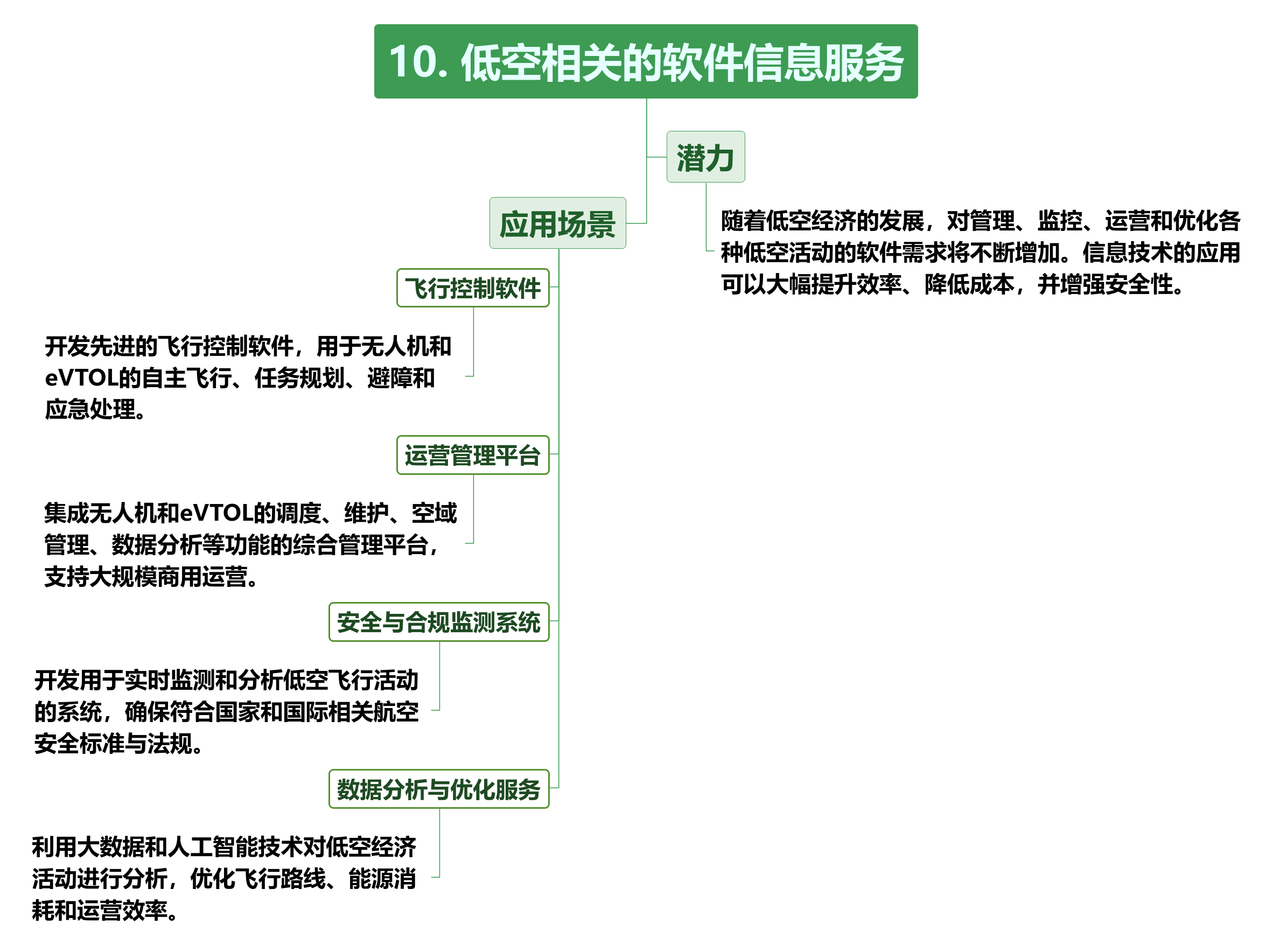
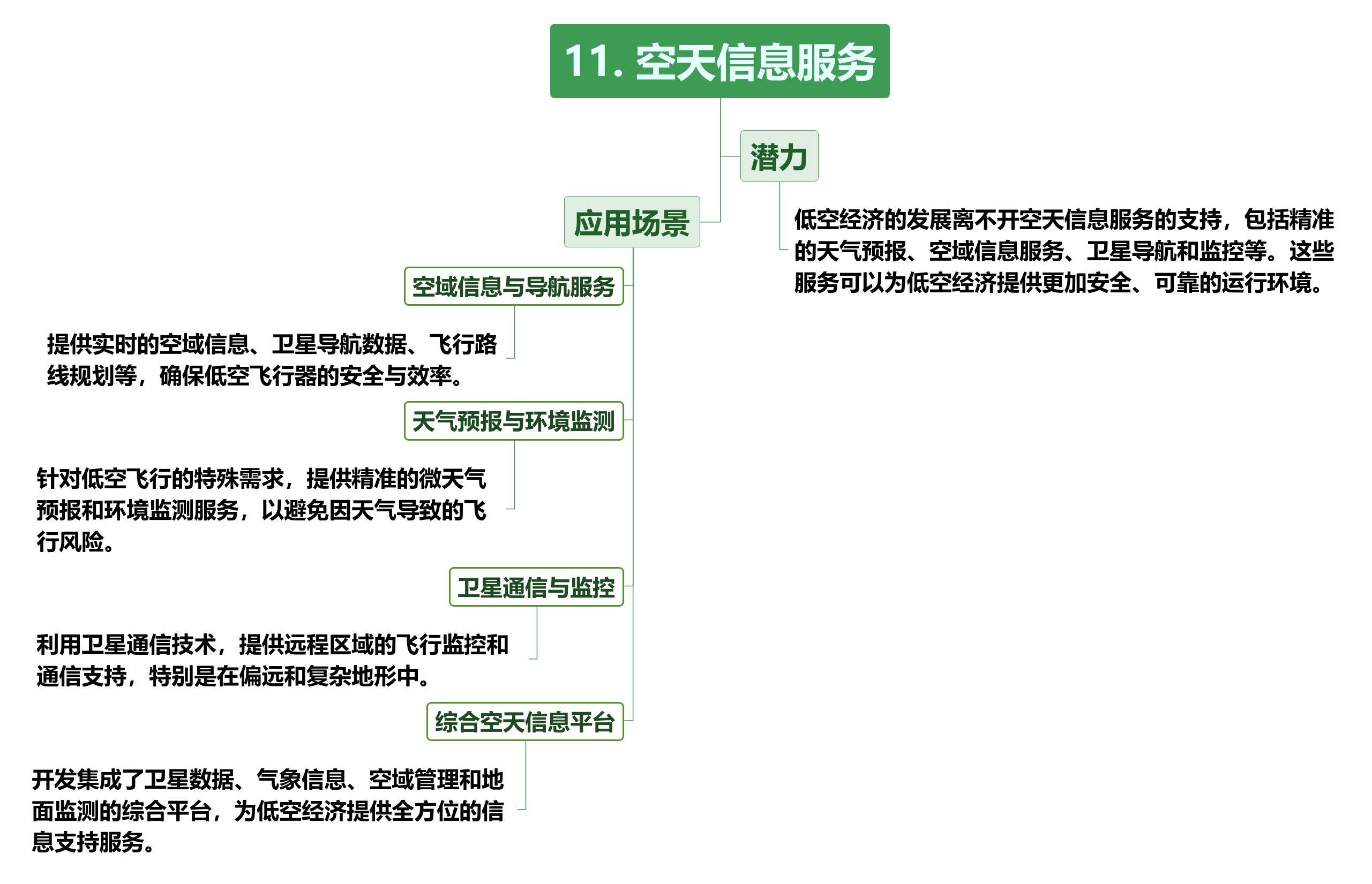
These infrastructures and information services are not only necessary conditions for the development of the low-altitude economy, but will also become an important force in promoting the industrialization of the low-altitude economy. By building a complete infrastructure and information service system, the low-altitude economy can better integrate aviation resources at the urban, regional and national levels, promoting the sustainable development of the entire industry.
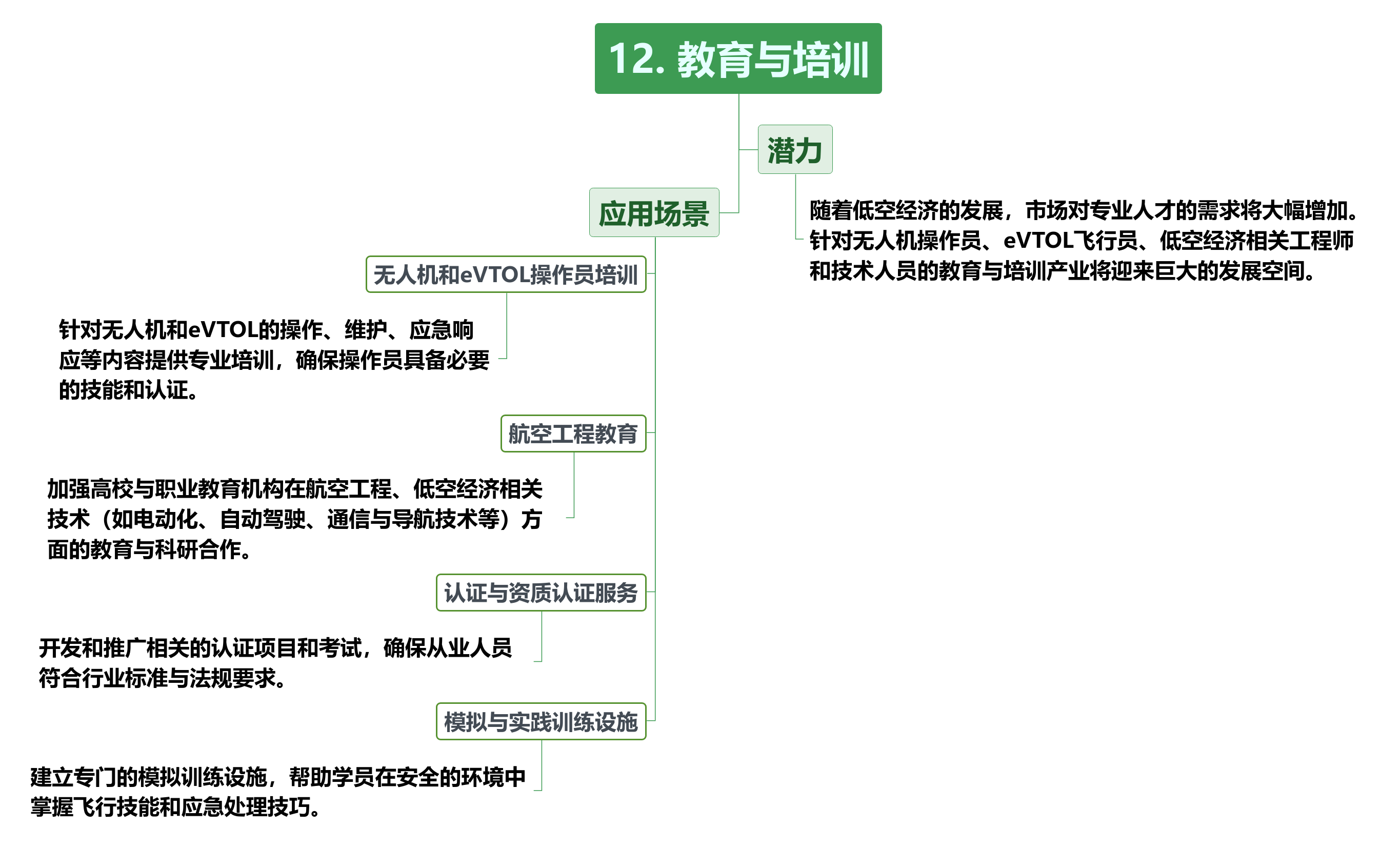
This direction will provide continuous talent support for the development of the low-altitude economy industry, ensure the professionalization and safety of the industry, and promote the healthy development of the low-altitude economy. Through comprehensive development covering multiple aspects such as education and training, infrastructure construction, and software information services, the low-altitude economy will form a complete ecosystem with strong vitality and broad application prospects.
02
The current situation of low-altitude economic development in our country
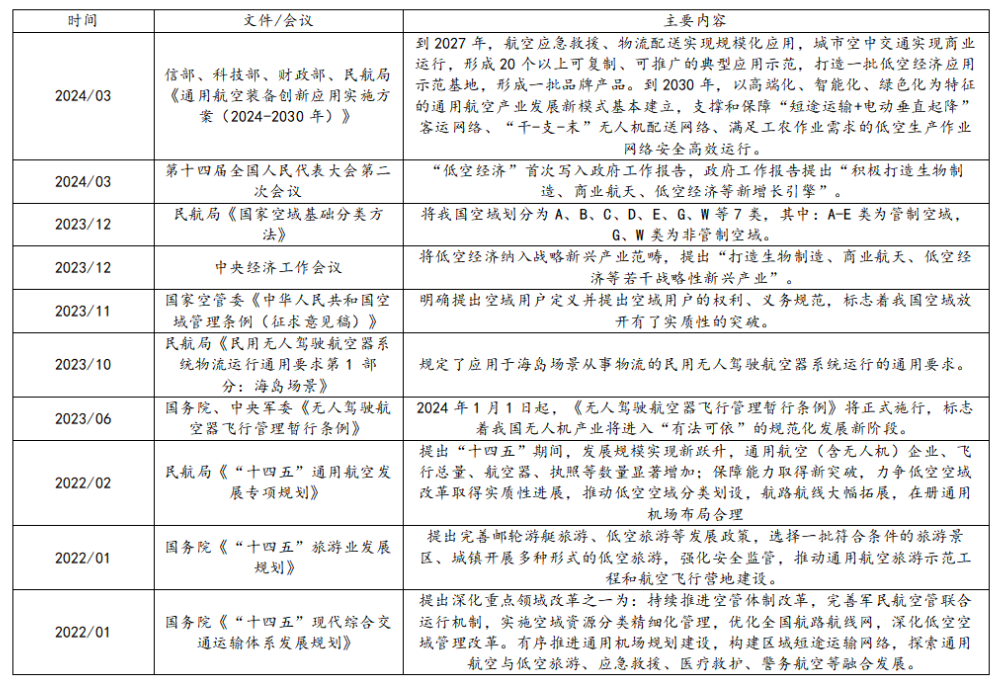
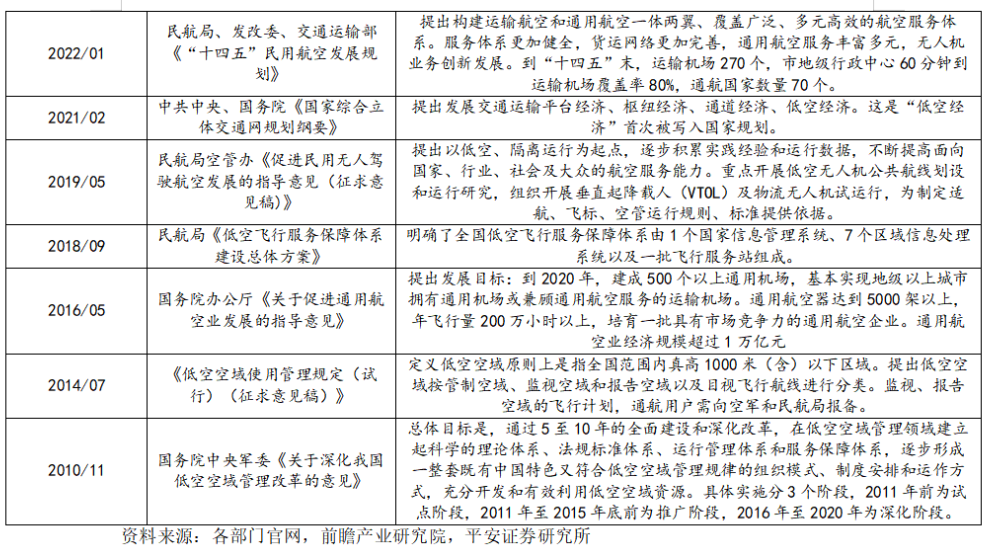
The policy development process of low-altitude economy in our country
The policy development process of low-altitude economy can be traced back to 2010, when it mainly focused on specific fields such as military reconnaissance and attack. The limitations of technology and policy restricted the development of low-altitude flight. In February 2021, the "National Comprehensive Three-Dimensional Transport Network Planning Outline" issued by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and The State Council included the concept of "low-altitude economy" in the national plan for the first time, marking that the low-altitude economy has officially been elevated to a national strategy.

In December 2023, the Central Economic Work Conference proposed to develop strategic emerging industries including low-altitude economy and included low-altitude economy in the 2024 government work report, highlighting the significant position of low-altitude economy in the countrys economic development.
Local governments have also actively responded to the central governments policies and have successively introduced relevant policy measures. For instance, in 2020, Hunan Province became the first province in the country to expand its pilot program for low-altitude airspace management reform and has introduced a number of policies focusing on industrial development and market cultivation. Since 2022, Shenzhen has successively issued the "Implementation Plan for the Innovative Development of Low-altitude Economy Industry in Shenzhen (2022-2025)" and the "Several Measures of Shenzhen to Support the High-Quality Development of Low-altitude Economy", and formulated the first regulation on low-altitude economy in the country.

In addition, local governments are constantly optimizing the development environment for the low-altitude economy. For instance, Guangzhou has formulated the "Implementation Plan for the Development of Low-altitude Economy in Guangzhou", promoting the top-level design of the low-altitude economy, the construction and application of a full-space unmanned system in a coordinated manner, and assisting in establishing a collaborative management mechanism among the military, local authorities and civilians. Suzhou City has released the "Implementation Plan for High-Quality Development of Low-altitude Economy in Suzhou City (2024-2026)", aiming to promote intensive innovation and rapid growth of the low-altitude economy industry.
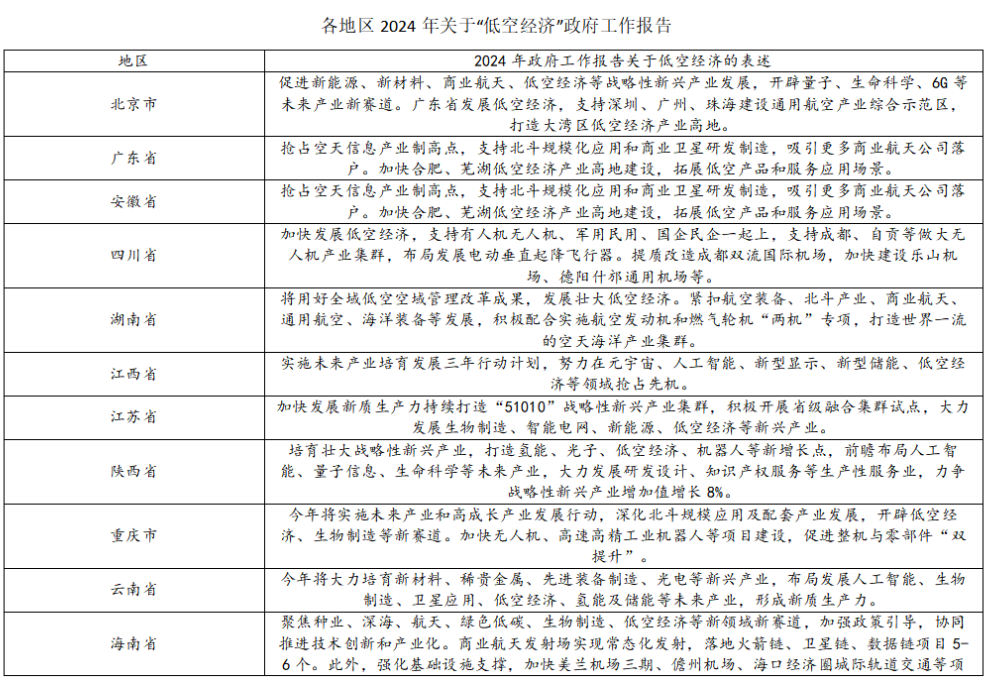
At the beginning of 2024, many local governments included "low-altitude economy" in their local government work reports. According to incomplete statistics, 17 provinces (municipalities directly under the Central Government and autonomous regions) have included the relevant content of "low-altitude economy" in their government work reports, namely Beijing, Guangdong, Anhui, Sichuan, Hunan, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Shaanxi, Chongqing, Yunnan, Hainan, Shandong, Henan, Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning and Fujian. In addition, the government work reports of 10 provinces (municipalities directly under the Central Government and autonomous regions), namely Shanghai, Tianjin, Hebei, Guizhou, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Gansu, Qinghai, Xizang and Xinjiang, also cover the content related to low-altitude economy. Moreover, cities such as Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Chengdu, Suzhou, Zhuhai and Ganzhou have included low-altitude economy in the government work reports of their prefecture-level cities.
Overall, the policy development of the low-altitude economy has undergone an evolution from early technological exploration to standardized development, and now to the current stage of widespread application. The policy support from the national and local governments has provided a solid foundation for the rapid development of the low-altitude economy, promoting the improvement of the industrial chain and technological progress.
Chart: Review of Chinas National-level Low-altitude Economic Policies

The planning of low-altitude economy in key provinces and cities of our country
Beijing
Industrial positioning: Cultivate the low-altitude economy into a leading and exemplary industry that leads the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, and build a capital of industrial innovation for the low-altitude economy and a national demonstration zone for the low-altitude economy.
Industrial goal: Within three years, the number of enterprises related to the low-altitude economy will exceed 5,000. It aims to become a leading and exemplary enterprise in the country in areas such as technological innovation, standard policies, application demands, and security countermeasures, driving the citys economic growth to exceed 100 billion yuan. By 2027, 10 leading enterprises with an annual revenue of over 1 billion yuan, 50 core supporting enterprises in industrial chains with an annual revenue of over 100 million yuan, and 100 technology service enterprises will be cultivated.
Shanghai
Industrial positioning: Jointly build with cities in the Yangtze River Delta to become one of the first batch of low-altitude inter-provincial general aviation cities in China, establish a comprehensive demonstration and leading area for the national low-altitude economic industry, and accelerate the creation of a "Sky City" with international influence.
Industrial goals: By 2027, a complete industrial system covering the research and development, design, final assembly and manufacturing, airworthiness testing, and commercial application of new low-altitude aircraft will be established. A highland for industrial innovation, commercial application, and operation services in the low-altitude economy will be created. The core industry scale will reach over 50 billion yuan, and the company will take the lead in the global innovation and development of the low-altitude economy.
Guangdong Province
Industrial positioning: Relying on the three core cities of low-altitude economy, namely Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Zhuhai, to strengthen leading support, leverage the manufacturing support advantages of cities such as Foshan, Jiangmen, Huizhou, Dongguan and Zhongshan, promote the creation of low-altitude application scenarios in accordance with local conditions in the eastern, western and northern regions of Guangdong Province, and cultivate a low-altitude economy industrial cluster with global competitiveness.
Industrial goal: By 2026, the scale of the low-altitude economy will exceed 300 billion yuan, and a low-altitude economy industrial pattern featuring the three-core linkage of Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Zhuhai, multi-point support and large-scale development will be basically formed. A number of leading enterprises and specialized, refined, distinctive and innovative enterprises will be cultivated, and the industrial scale will grow steadily. The total flight hours of general aircraft in the province have reached 150,000 hours, and progress has been made in pilot demonstrations of urban air traffic, low-altitude logistics, and unmanned systems in all Spaces.
Zhejiang Province
Industrial positioning: Centered on the Hangzhou and Ningbo National Airport Economic Demonstration Zones, it will link up with Jiaxing and Shaoxing, radiate to Taizhou, and build an airport economic belt around Hangzhou Bay. Build provincial-level airport economic zones in Wenzhou, Jiaxing and Jinhua-Yiwu.
Industrial goal: By 2027, a high-level civil aviation strong province and a highland for low-altitude economic development will be basically established, featuring provincial-wide coverage of aviation services, globally accessible route networks, multi-modal and convenient airport hubs, high-energy agglomeration of the aviation industry, leading role in low-altitude economy, and smooth and efficient industry governance. More than 150 public unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) take-off and landing fields will be built, covering the core areas of the four major metropolitan areas. General aviation routes will reach the Yangtze River Delta region, and UAV logistics routes will basically cover the core areas of the four major metropolitan areas, achieving an annual low-altitude flight volume of 2 million hours. By 2035, a high-level civil aviation power province and a highland for low-altitude economic development will be fully established.
Jiangsu Province
Industrial positioning: To build a leading and demonstration area for the innovative development of the low-altitude economy industry across the country, with its development level consistently ranking among the top in the nation.
Industrial goal: Strive to increase the scale of the citys low-altitude economic industry to over 50 billion yuan through three years of construction. In the next three years, more than 240 low-altitude aircraft take-off and landing fields (points) and their supporting information infrastructure will be built, more than three test flight fields and operator training points will be established, one to two general aviation airports will be planned and constructed, and more than 120 low-altitude routes will be opened.
Shandong Province
Industrial positioning: Treat it as a strategic emerging industry, build a low-altitude economic system with Shandong characteristics, create an important source of innovation and development for the national low-altitude economy, and make it an important growth pole for the high-quality development of the provincial economy.
Industrial goal: By 2026, the provinces low-altitude economic service and guarantee level will be leading in the country, its innovation capacity will be world-class, application scenarios will be rich and diverse, and the industrial level will be significantly upgraded. It will become an important source of innovation and development for the low-altitude economy in the country, and the low-altitude economic industry will become an important growth pole for the high-quality development of the provinces economy. Cultivate more than 20 leading enterprises with annual revenue of over 100 million yuan, more than 50 specialized, refined, distinctive and innovative enterprises, and more than 300 enterprises on the industrial chain, and build a low-altitude economic industrial development pattern led by the two cores of Jinan and Qingdao and supported by the four points of Yantai, Dongying, Rizhao and Binzhou.
Anhui Province
Industrial positioning: Seize the opportunities presented by the reform of low-altitude airspace, technological innovation and large-scale application, accelerate the cultivation and development of low-altitude economy in Anhui Province, promote the formation of a development pattern featuring the integration of low-altitude manufacturing and services, mutual promotion between application and industry, and coordinated interaction with distinct characteristics, and build a low-altitude economic development highland with significant influence.
Industrial goals: By 2025, the construction of low-altitude infrastructure will be accelerated, a number of application demonstration scenarios will be established, the scale and innovation capacity of the low-altitude economy will be rapidly enhanced, and an initial agglomeration industrial ecosystem will be formed. By 2027, low-altitude infrastructure will be further improved, application scenarios will be continuously expanded, the scale and innovation capacity of the low-altitude economy will reach the leading level in the country, and a low-altitude economic development pattern featuring dual-core linkage, multi-point support and large-scale development will be formed. Specific goals include building a certain number of general airports and temporary take-off and landing sites as well as take-off and landing points, expanding the scale of the low-altitude economy, increasing the number of large-scale enterprises, fostering ecological-leading enterprises, enhancing innovation capabilities, increasing the number of provincial-level or above scientific and technological innovation and public service platforms, extending the flight duration of general aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles, and improving the industrial ecosystem, etc.
Hunan Province
Industrial objective: Fully unleash the driving force of the reform of low-altitude airspace management and strive to build a national demonstration province for low-altitude economic development. By 2025, the province aims to have over 20 large-scale enterprises in the low-altitude economy sector, with the total output value of the low-altitude economy reaching approximately 160 billion yuan.
Policies on low-altitude economic industries in key provinces and cities
Beijing
The Beijing Municipal Commission of Economy and Information Technology has released the "Action Plan for Promoting High-Quality Development of Low-altitude Economic Industries in Beijing (2024-2027) (Draft for Public Comment)", making layouts in application scenarios such as emergency rescue, logistics distribution, air ferries, intercity commuting, and characteristic cultural tourism, and clarifying the direction of industrial chain layout. It covers the research and development of advanced complete machines, the matching of core components and materials, and the development of airborne air traffic control and other equipment.
Shanghai
The General Office of the Shanghai Municipal Government has officially issued the "Action Plan for High-Quality Development of the Low-altitude Economy Industry in Shanghai (2024-2027)", providing support for the development of the low-altitude economy industry in aspects such as the cultivation of leading enterprises, the supply of key supporting facilities, the construction of software and hardware facilities, the creation of spatial carriers, the improvement of management services, and the promotion of commercial scenarios.
Guangdong Province
The General Office of the Peoples Government of Guangdong Province has issued the "Action Plan for Promoting High-Quality Development of Low-altitude Economy in Guangdong Province (2024-2026)". The main measures are as follows: promoting the reform of low-altitude airspace management, making advanced plans for low-altitude infrastructure, expanding low-altitude application scenarios, enhancing the innovation capacity of low-altitude industries, and building low-altitude industrial manufacturing bases, etc.
Zhejiang Province
The Peoples Government of Zhejiang Province has issued the "Several Opinions on Building a Strong Civil Aviation Province at a High Level and Creating a High Ground for Low-altitude Economic Development", providing support for airport infrastructure projects that meet the conditions through funds such as the Civil Aviation Development Fund, central budgetary investment, ultra-long-term special Treasury bonds, and local government special bonds. Encourage social capital to participate in the investment and construction of airport infrastructure and supporting service facilities, and broaden the sources of construction funds.
Jiangsu Province
The main industrial policies for low-altitude economy in various regions of Jiangsu Province include: Nanjing City has issued the "Implementation Plan for Promoting High-Quality Development of Low-altitude Economy in Nanjing City (2024-2026)" and the "Several Measures of Nanjing City on Supporting High-Quality Development of Low-altitude Economy (Trial)" Suzhou City has introduced 15 specific measures, including encouraging low-altitude technological innovation to lead the way, introducing and cultivating key low-altitude enterprises, expanding low-altitude flight application scenarios, and optimizing the development environment for the low-altitude economy. Yangzhou City has released the "Implementation Opinions on High-Quality Development of Low-altitude Economy in Yangzhou City". Changzhou City has released the "Three-Year Action Plan for High-Quality Development of Low-altitude Economy in Changzhou City (2024-2026)".
Shandong Province
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of Shandong Province and three other departments have issued the "Implementation Plan for the Innovative Application of General Aviation Equipment (2024-2030)" (No. 52 of 2024 issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the Ministry of Heavy Industry), seizing the strategic opportunity of intensive innovation and rapid growth in the low-altitude economy industry, and creating new driving forces for the innovative development of general aviation equipment.
Anhui Province
The Development and Reform Commission of Anhui Province has issued the Implementation Plan for Accelerating the Cultivation and Development of Low-altitude Economy in Anhui Province (2024-2027) and several measures, mainly promoting the development of the low-altitude economy industry through the construction of low-altitude infrastructure, expanding the low-altitude operation service market, and enhancing the innovation capacity of the low-altitude economy.
Hunan Province
The General Office of the Peoples Government of Hunan Province has issued the "Several Policy Measures on Supporting the High-Quality Development of the Low-altitude Economy throughout the Province", supporting the high-quality development of the low-altitude economy in the province from 12 aspects. The main contents include: Subsidies will be increased in areas such as traditional general aviation operations, enhanced operation of new aircraft, attraction of low-altitude enterprises, and establishment of technological innovation platforms in the low-altitude economy, with the maximum policy subsidy reaching 10 million yuan.
03
The development prospects and future trends of Chinas low-altitude economy
In recent years, Chinas low-altitude economic industry has grown rapidly, and the market scale has continued to expand. According to external data and analysis reports, the market size of Chinas low-altitude economy exceeded 500 billion yuan in 2023, reaching 505.95 billion yuan, with a year-on-year growth rate as high as 33.8%. It is expected that by 2026, the market size will exceed one trillion yuan. The low-altitude economic industrial chain has initially taken shape, covering multiple links such as aircraft research and development and manufacturing, flight service support, and infrastructure construction.
The low-altitude economy is mainly characterized by a "combined" economic form. This new economic form has the following development trends in terms of products, industrial systems, administrative systems, and regional integration:
Product equipment
As a sub-sector of the future air transportation industry, eVTOL is one of the most popular new fields in high-end manufacturing and an important trend in the future development of low-altitude economy. In 2023, driven by the low-altitude economy policy and the accelerated commercialization process of eVTOL, the scale of Chinas eVTOL industry reached 980 million yuan, with a year-on-year growth of 77.3%. In terms of regional distribution, it is mainly concentrated in Central South and East China. North China, Southwest China, Northeast China and Northwest China mainly focus on related complete machine tests and key system support. The overall industrial scale of the four regions is around 300 million yuan. It is expected that the eVTOL industry will witness its first round of commercial explosion in 2024, with a significant increase in scale. With the accelerated advancement of airworthiness certification for multiple aircraft models, it will maintain a relatively high growth rate and is projected to reach 9.5 billion yuan by 2026. In addition, the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) industry is gradually improving. Coupled with mature 5G technology, big data, cloud computing and Internet of Things technology, UAVs will become a powerful tool for expanding new scenarios and business forms in the low-altitude economy.

Industrial system
In the future, the new general aviation industry will form an industrial supporting system oriented towards green and electric, an operation support system represented by low-altitude intelligent connection, an infrastructure system characterized by vertical volume, a regulatory service system aimed at safety and controllability, and an industrial organization system with cross-border integration as the trend. All application scenarios will be coordinated as a whole due to the development of the low-altitude economy and develop in a coordinated manner under unified command and dispatch.
Administrative approval
Under the dual drive of the government and the market, the low-altitude economy will fully leverage the role of various forms of ownership, forming a favorable situation where each has its own characteristics, supports each other and develops in an integrated manner. In addition, the Civil Aviation Airworthiness Certification centers of China in various regions will actively innovate in airworthiness standards, compliance methods, regulatory standards, and airworthiness certification models to enhance the efficiency of airworthiness certification work.
Regional integration
In the future, low-altitude economy will become the key to regional integration. The continuous deepening of low-altitude airspace reform is conducive to enhancing the regional service supply capacity. For instance, enhancing the efficiency of intercity transportation, shortening commuting time, reducing the circulation time of goods, and building smart city services for drones, a logistics transportation service system for drones, and comprehensive applications of drones in the ocean, etc. It is conducive to the integration of urban and rural economies and enhances the efficiency of rural transportation.
04
The pain points of the development of low-altitude economy in our country
Top-level design
The laws and regulations concerning the emerging business forms of the low-altitude economy are not yet complete, and the contents of some rules and standards are not in line with the current situation. The construction and management of general aviation airports have long followed the standards for air transport airports, with excessively high approval levels and long processing periods. The statistical standard system for low-altitude economy is lacking, and there is a lack of statistics on the main indicators of low-altitude economy.
Technological development
The domestic production capacity of related core components such as main control chips and precision components still needs to be enhanced. The shortcomings of drones in terms of safety, endurance, load capacity, obstacle avoidance and noise reduction still exist. Key core technologies such as flight control, intelligent obstacle avoidance, and fault diagnosis need to be broken through. Low-altitude network services still need to be optimized. A large number of existing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) still rely on single-point communication with ground stations, which limits the flexibility and autonomy of UAV aerial operations.
Application Management
Most general aviation operation enterprises lack mature business models and stable profit models, and the development of market demand is insufficient. The production and service activities in the fields that the low-altitude economy has entered are relatively shallow in level and the industrial chain is relatively short. Many fields are still blank.
Airspace management
A comprehensive assessment mechanism for the safety, efficiency, economy and fairness of low-altitude airspace flights still needs to be established. Lack of refined airspace management techniques and means; Some flight service stations have failed to provide effective services due to the lack of sufficient support from both military and civil aviation.

05
Suggestions for the Development of Low-altitude Economy in Our Country
Focus on "new" low-altitude equipment
Low-altitude aircraft are the main hardware carriers for completing various low-altitude flight activities and ensuring the safe, convenient and efficient completion of all tasks. Possessing advanced low-altitude aircraft is one of the prerequisites for promoting the development of the low-altitude economy. The key to grasping the "newness" of low-altitude equipment lies in taking the technological, power and operational system changes in the manufacturing of low-altitude aircraft as the main line, and strengthening the research and application of new types of low-altitude aircraft.
Focus on "new" low-altitude scenarios
The various application scenarios brought about by the full development and utilization of low-altitude airspace will become increasingly diverse. The fields such as low-altitude cargo transportation by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), urban air transportation by eVTOL, and public services by civil helicopters have broad prospects. The key to promoting the development of the low-altitude economy lies in continuously following up and exploring new scenarios, grasping the new achievements of low-altitude applications, fully tapping into the demands of ones own scenarios, coordinating element resources, and promoting the implementation of related applications to form a demonstration and promotion situation.
Focus on "new" infrastructure
Low-altitude infrastructure is the cornerstone for promoting the development of the low-altitude economy and a prerequisite for fully meeting the flight requirements and regulatory needs of various low-altitude aircraft. Grasp the "new" changes in low-altitude infrastructure, accelerate the construction of a three-level linkage low-altitude intelligent network at the provincial, municipal and district (county) levels, new low-altitude aircraft take-off and landing facilities, and proactively plan and layout new low-altitude infrastructure such as energy facilities for new energy aircraft.
Article source: Zhongguancun Smart City Informationization Industry Alliance, State-owned Assets Progress Bar























